Extraction Methods of Biopsies
Touch DNA is increasingly being used in forensic work, making it crucial to understand its precise nature, including its origins and components. Recent research shows that cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is a critical component of touch DNA samples, and recovery and purification of this material are essential for obtaining valuable genetic information.
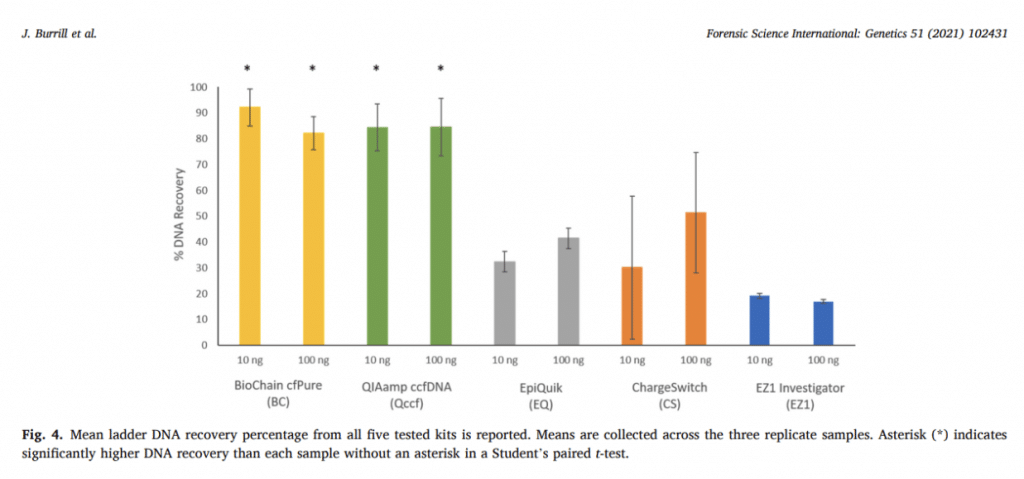
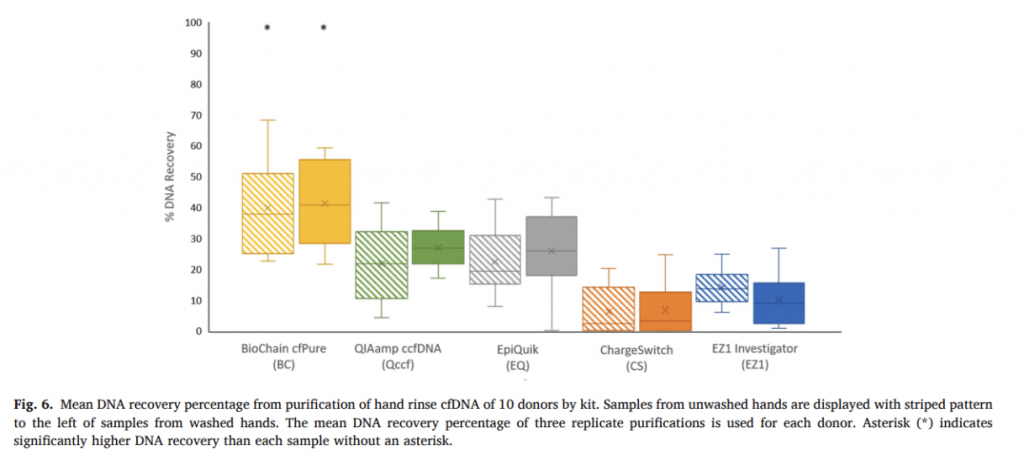
The recovery of cfDNA is best achieved through size-targeting methods, as the DNA is highly fragmented. Burrill et al. (2021) found Biochain’s cfPure kit to be the most successful among the kits available in the market.
Improving the recovery and purification of cfDNA is critical to the development of fragmented cfDNA as a valuable source of genetic information in future analyses. It may also be important to reassess allele frequencies if DNA profiles can be derived from extracellular fragmented DNA.
In conclusion, the recovery and purification of cfDNA from touch DNA samples is crucial for obtaining valuable genetic information in forensic work. Our cfPure kit uses centrifugation and size-targeting methods which have been found to be effective in isolating and purifying cfDNA. However, further research is needed to develop more targeted and efficient purification methods for hand-rinse samples and control ladder DNA. The use of fragmented cfDNA may have significant implications for forensic investigations and requires continued study.
Related Products
Check out Biochain’s cfPure kits here: cfDNA Kit, cfPure® | BioChain Institute Inc.
The cfPure® Cell-Free DNA Extraction Kit is BioChain’s magnetic bead-based DNA extraction kit. It is designed to isolate circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from plasma, serum, and urine. This cfDNA kit touts a simple and automation-friendly protocol that allows users to quickly extract from a range of sample volumes, high-quality downstream-ready cfDNA. Extract high-quality cell-free DNA from plasma, serum, and urine for Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), Bisulfite Sequencing, PCR, qPCR, ddPCR, and other demanding applications.
References
Burrill J, Kombara A, Daniel B, Frascione N. Exploration of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) recovery for touch deposits. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2021 Mar;51:102431. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2020.102431. Epub 2020 Nov 26. PMID: 33260058.