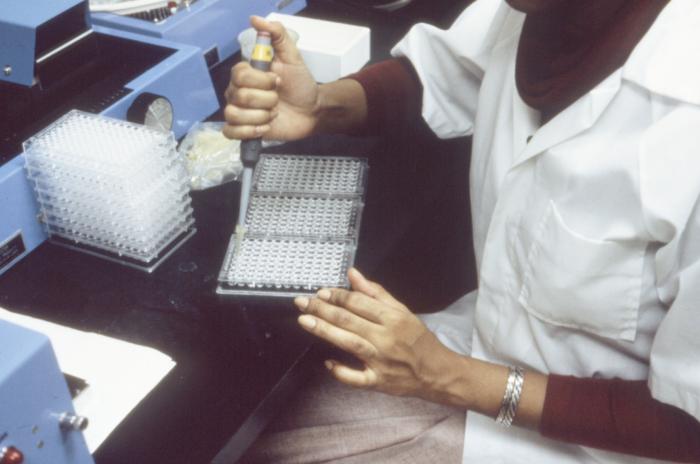
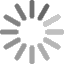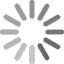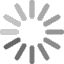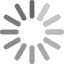
ELISA Test Procedures
The enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a highly sensitive test that detects and measures antibodies, neurobiological analytes, cytokines and phosphorylated proteins in blood which are molecules of interest in research labs.
Applications For ELISA
This test is used as a screening tool and is used to determine the presence of antibodies for certain disease conditions in the blood. Antibodies are immunological proteins produced by the body in response to various pathogenic antigens that enter the body. Some of the diseases that can be detected using ELISA includes HIV infection, HPV, Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium (Lyme disease), Varicella virus (chickenpox and shingles), zika virus, Rotavirus, and squamous cell carcinoma, to name a few. The ELISA kit works fast and is simple to carry out. ELISA has been used commonly in-home pregnancy tests and in the food industry to detect food allergens such as walnuts, peanuts, milk, almond and eggs. It can process multiple samples in parallel and is a popular diagnostic tool used in detecting antibody presence in blood samples.
Basic Principle of ELISA
ELISA is performed in a polystyrene plate consisting of 96 wells or 384 wells. The reagents in the ELISA test are immobilized and this makes the procedure easy to perform. The assay has a monoclonal antibody coat on the microtiter plate. The preferred antibody is IgG which is purified and is used in conjugate to avoid interference from other proteins when binding with the enzyme. When the blood sample is added, the specific antibody (primary antibody) adheres to the protein of interest (e.g. a cytokine).
A secondary monoclonal antibody binds to a different epitope on the protein. The assay is labelled with biotin which allows for subsequent binding of a protein such as strepvidin- conjugated enzyme. Commonly used enzymes in this procedure are horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and alkaline phosphatase (AP). Any unbound reagents/serum components are eliminated by thorough washing of the plate. PBS-T (Phosphate buffered saline with Tween) is used as the diluent for removing unbound molecules.
A chromogenic substrate, such as Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB), is used for staining. It is added to the assay which develops a color based on the enzymatic reaction (it is directly proportional to the amount of antigen bound). The choice of the substrate depends on the type of instrumentation (spectrophotometer, fluorometer and luminometer) used. The enzyme has a fluorescent tag that converts the substrate to a product that is detectable by a fluorometer. The concentration of the protein is determined by a standard curve of known protein concentrations. Mean absorbance is calculated for the standard, controls and the samples. A standard curve is constructed by plotting the mean absorbance on the Y axis vs concentration on the X axis or using computer software programs. The optical densities can be measured at different target wavelengths using an ELISA plate reader.
Types of ELISA
There are three types of ELISA assays used. Direct, indirect, and sandwich assays.
Direct ELISA Procedure
- Antigen is coated onto the wells by passive adsorption and incubation
- Bovine serum albumin is used to block the other binding sites
- The plates are washed with PBS-T three times to remove unbound molecules.
- Biotinylated Antibody (the enzyme conjugated antibody) IgG with Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) is added and incubated.
- The wells are washed again with PBS-T to remove unbound molecules.
- Chromophore substrate (TMB) is added which detects the presence of the enzyme and thus the antigen.
Indirect ELISA Procedure
- Antigen is coated onto the wells by passive adsorption and incubation
- The plate is washed with PBS to remove unbound antigens.
- Bovine serum albumin is used to block the other protein binding sites
- Primary sample antibody is added to the plate and incubated with the antigen.
- The plates are washed with PBS to remove unbound molecules.
- The secondary enzyme conjugated antibody is added and incubated with the antigen.
- Wells are washed to remove unbound molecules.
- Chromophore substrate is added which detects the presence of the enzyme and thus the antigen.
Sandwich ELISA Procedure
- The plate is prepared and a known quantity of capture unlabeled monoclonal antibodies are added to the wells and incubated.
- The antigen containing sample is then added to the plate
- The plates are washed to remove unbound molecules.
- The primary antibodies are then added and incubated with the antigens.
- The plate is washed to remove unbound primary antibodies.
- Secondary antibody (the enzyme conjugated antibody) with Avidin Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or alkaline phosphatase (AP) is added and incubated.
- The streptavidin labeled enzyme is added; it binds to the biotinylated detection antibody.
- The plates are washed so the unbound enzyme linked antibodies are removed.
- The chromophore substrates are added and incubated and it changes to a blue color depending on the amount of bound analyte.
- Stop solution containing an acid (sulfuric acid) is added which terminates the reaction and the color changes to yellow. The wells are then read at 450nm.
ELISA can be performed with multiple modifications to the procedure to achieve accurate results. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages.
High Quality Detection with BioChain’s ELISA Kits
BioChain offers products with accurate and reliable results. The kits are rigorously quality tested to maximize molecule detection sensitivity. The ELISA Kits are competitively priced due to the need for multiple kits to test individual viruses.
These proprietary kits are designed to produce rapid results with user-friendly protocols and automation capabilities. The ELISA Kit detects a wide range of infectious agents, including HIV, HBV, HCV, and Herpes Simplex Virus Type II. Featuring high sensitivity and specificity, the kit’s downstream applications include diagnostic research.
These replicable and consistent tests are conventional immunological assays containing purified antibodies. The serum sample, antigen, and peroxidase-conjugated antibodies are coated on the solid phase of multi-wells:
- ELISA Kit for Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
- ELISA Kit for IgM Antibody to Hepatitis B Core Antigen
- ELISA Kit for Hepatitis B e Antigen
- ELISA Kit for Antibody to Hepatitis B Core Antigen
This kit is coated with murine anti-HIV-1 p24 antibodies. Exposure will detect test specimens containing p24 reactive determinants. The assay indicates levels present for HIV p24, HAV, HBV, HCV, HEV, and TORCH: