An Introduction into Detecting Viruses: ELISA and HPV
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a biochemical technique used in immunology to identify substances that portray antigenic properties that are present in a test subject’s bodily fluids. ELISA detects proteins instead of other small molecules, like glucose and potassium. This safe and easily reproduced technique has revolutionized the way people screen for viruses including the human papillomavirus (HPV); one of the leading causes of cervical cancer
Cancer and HPV
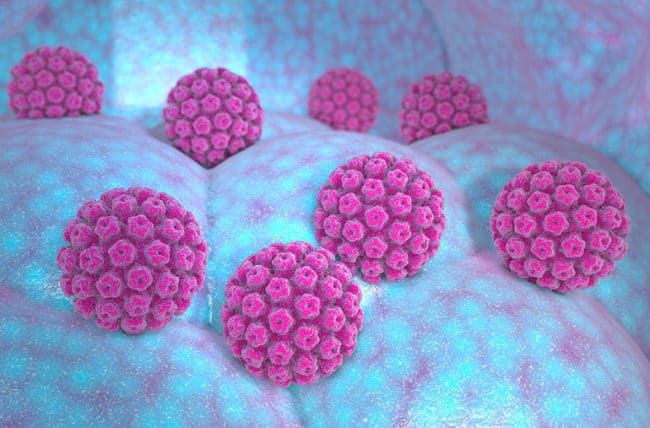
Genetic sequencing has uncovered over 100 different strains of HPV. Of those strains, 15 are oncogenic, including HPV-16 and HPV-18. Roughly 11-12% of the global population carries a strain of the virus. Most of the time an infection from HPV does not result in cancer, however when a cancerous strain is contracted, it becomes paramount that a the virus is detected and managed.
In the 1960’s many countries started screening women for cervical cancer and the HPV virus. Since screening women for HPV and cervical cancer became more prevalent, coupled with the practice of administering vaccines, the mortality rate of cervical cancer has dramatically decreased. Despite these efforts, cervical cancer is still one of the most common forms of cancer contracted by women.
In 2017, the American Society of Clinical Oncology estimated that there were about 12,820 new cases of diagnosed invasive cervical cancer. 4,210 women are expected to die from cervical cancer in 2017. Screening women at regular doctor visits via the Pap smear is a great first step in identifying potentially harmful HPV strains, however ELISA is a more comprehensive and accurate testing tool.
History of ELISA
ELISA revolutionized the detection method by providing a quick and safe technique that is often completed in only hours or minutes with an ELISA kit. Prior to the 1970’s, the only test available for antibody detection was radioimmunoassay (RIA) which used radioactively-labeled antigens. Under the RIA method, detecting viruses was time consuming and dangerous. Scientists, driven by the desire to find a safer testing method, began experimenting with enzyme labels in immunoassay. Linking an enzyme to an antibody or antigen without manipulating the biological activity in conjugating reaction was thought to be impossible. This perception did not stop some researchers from experimenting.
ELISA was invented by two Swedish scientists, Eva Engvall and Peter Perlman.
They published their first paper in 1971 and presented ELISA as a replacement for radioimmunoassays.
Discerning HPV With ELISA
During this last decade, researchers have developed, tested, and verified with experimentation serological assays for HPV based on virus-like particles. One of the most established biomarkers of viral infection is the detection of virus-specific antibodies.
Researches associated with the American Society for Microbiology have found that when ELISA is used for viral antibody detection, this technique will procure greater precision than other standard methods used for measuring immunoglobulins.
Research and the Future
The ELISA technique is a great starting point for virus detection. Just as there are many different kinds of viruses, there are many different versions of ELISA.
Scientists are constantly looking at improving detecting techniques. Researchers at OncoHealth Corporation and University of California have developed a unique, whole-cell ELISA based on a general anti-human HPV E6 antibody. This version of ELISA can specifically detect cervical precancers and cancer signs. The researchers' goal was to make a simple and accurate method that can be used throughout the world.
BioChain: Ease and Convenience
BioChain offers an extensive list of ELISA kits for research use of detection of infectious diseases, such as HBV, HCV, and HIV. The kits are approved and used in clinical diagnosis in other countries, such as China.
BioChain EPO ELISA is intended for the quantitative determination of Erythropoietin (EPO) in human serum.
Author
BioChain Institute Inc.